Zero Trust Section
Why Zero Trust?
To verify a technician,
Text #verify to (438) 800-2151
Social engineering attacks targeting individuals and businesses are on the rise.
Malicious actors impersonate your IT service provider and attempt to gain access to your computer, server, or network.
By adhering to a Zero Trust policy, your staff should treat every incoming call from us with skepticism and immediately initiate the technician verification process. With a clearly defined and easily accessible procedure, you can have peace of mind in seconds, knowing that you are in contact with Connextek’s support team.
Connextek has a dedicated number for technician verification requests: (438) 800-2151.
The process couldn’t be simpler:
- Add Connextek as a designated contact in your phone (optional).
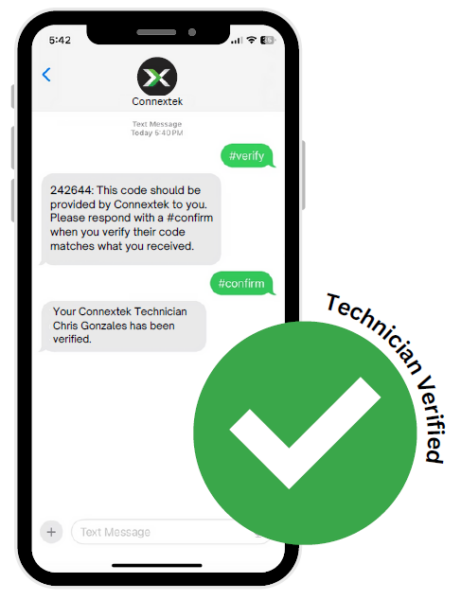
- From your mobile phone, send #verify to (438) 800-2151. Both you and the Connextek technician will receive the same randomly generated 6-digit code.
- The Connextek technician will verbally provide you with the 6-digit code. It must match the code you received.
- If the code matches, reply with #confirm to the designated number. If it doesn’t, you can hang up and call our support team directly or restart the process.
- You will receive an automatic message stating: “Technician verification successfully completed.”
To verify an end user (our clients)
What is end-user verification?
End-user verification is a set of identity verification techniques that confirm the identity of the individual in question. In the context of cybersecurity and access control, identity verification refers to the process of confirming and validating the identity of individuals attempting to access a system, application, or network. The goal is to ensure that only authorized users can access specific resources while preventing unauthorized or malicious actors from doing so.
Why does Connextek use end-user verification?
Connextek has adopted a Zero Trust Policy (ZTP). ZTP is a cybersecurity approach based on the principle that no entity—whether inside or outside the organization—should be trusted by default. This security model requires strict verification of anyone attempting to access network resources, regardless of their location or the device they are using.
Why Have We Adopted a Zero Trust Policy?
There are several reasons why we have implemented a Zero Trust Policy:
- Evolving Perimeter: Traditional security models rely on a secure perimeter, assuming that once someone is inside the network, they can be trusted. However, with the rise of remote work, cloud computing, and mobile devices, this concept has become less relevant. Zero Trust acknowledges that threats can come from both inside and outside the network.
- Advanced Threats: Traditional security measures are not always effective against advanced persistent threats and sophisticated cyberattacks, such as AI-driven voice phishing attacks. A Zero Trust approach helps mitigate these threats by continuously verifying and authenticating users.
- Data Security: As organizations increasingly store sensitive data in the cloud and enable remote access to their networks, protecting this data becomes critical. Zero Trust ensures that only authorized users can access specific data and resources, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Mobile Workforce: With a growing number of employees working remotely or using mobile devices to access company resources, the traditional trust model based on device location is no longer practical. Zero Trust treats every access attempt as potentially untrustworthy, regardless of the user’s location.
- Privileged Access: Zero Trust is particularly important for managing privileged access. Even employees with high-level access must continuously authenticate and prove their identity, reducing the risk of credential misuse.
- Insider Threats: While most employees are trustworthy, insider threats still pose a significant risk. Zero Trust minimizes potential damage by enforcing the principle of least privilege and continuous monitoring.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries require strict security and data protection standards. Adopting a Zero Trust policy helps organizations meet compliance requirements and demonstrate their commitment to securing sensitive information.
What Are Typical Methods for Authenticating Identity?
The goal of identity verification is to ensure that the person claiming a particular identity is indeed who they say they are. For effective verification, it relies on multifactor authentication (MFA). Here is a list of the factors we rely on:
- Something you know – This includes knowledge-based factors such as passwords, PINs, or security questions. These are often unavailable at the time of authentication due to forgotten information. Additionally, they can be compromised as they are frequently shared or based on easily accessible information (birthdates, addresses, etc.).
- Something you have – This includes possession-based factors such as security tokens, smart cards, or mobile devices. In the case of a mobile device, it typically involves the phone number and possession of the device as means of authentication, as they can be verified via a phone call, SMS, or push notification through an app.
- Something you are – This includes biometric factors such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or retina scans. With access to your mobile devices, your authenticated biometric information stored on the device serves as proof of something unique to the end user.
Verification by SMS
How does it work?
If we have a valid mobile phone number in our records, we can verify end-users via SMS. The phone number provided for all verification requests to Connextek is (438) 800-2151.
You will receive a six-digit code. Please repeat this six-digit code to your support technician within the specified timeframe.
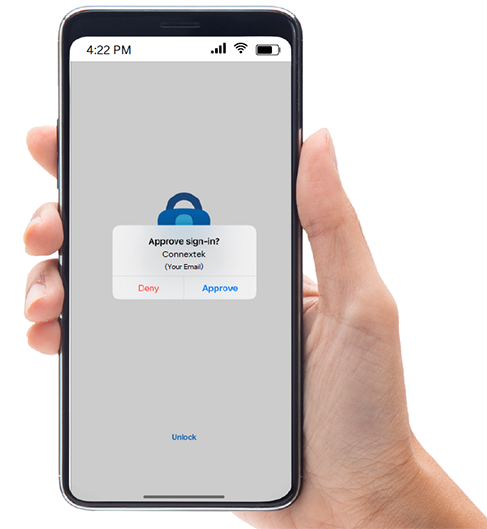
Microsoft Authenticator
How does it work?
If Microsoft Authenticator has been set up, please open the Microsoft Authenticator app on your mobile phone and click “Approve”.